Sciences such as geology, paleontology and archeology are very interested in identifying the age of objects found and these scientists sometimes use either relative dating or absolute dating to characterize the age of the objects they study. Before radiometric dating it was difficult to determine the actual age of an object.
If an archaeologist is studying past civilizations, the archaeologist may be able to say that in a particular location the ruins of once civilization were found to have been build on another and so the layers unearthed in an excavation convey the sequence of historical occupations without revealing the actual dates. If the archaeologist finds a sample suitable for carbon dating, then an absolute date may be assigned to an object.
Similarly for paleontologists who find layers of fossils. Radioactive isotopes can also be used by a paleontologists to assign an age to a fossil in some cases and that is an example of absolute dating with radiometric methods. For geologists, it is similar.
Geologists deal with the oldest of samples and radiometric dating with uranium is one of the few methods of absolute dating. What is the difference between relative-age dating and absolute-age dating? Relative compares the age of one event with that of another.
Relative Vs. Absolute Dating: The Ultimate Face-off
Absolute determines the actual age of the event. What is a similarity to relative and absolute dating? How are absolute dating and relative dating alike? What is the similarities between the relative dating and the absolute dating of a fossil and how are they used? It is the method of descovering the methodof the age of something I think it is the age of the fossil u are trying to find out. The difference between absolute and relative location? What is the difference between relative dating and numerical?
- dating for parents!
- dating website for fit singles!
- Absolute dating - Wikipedia.
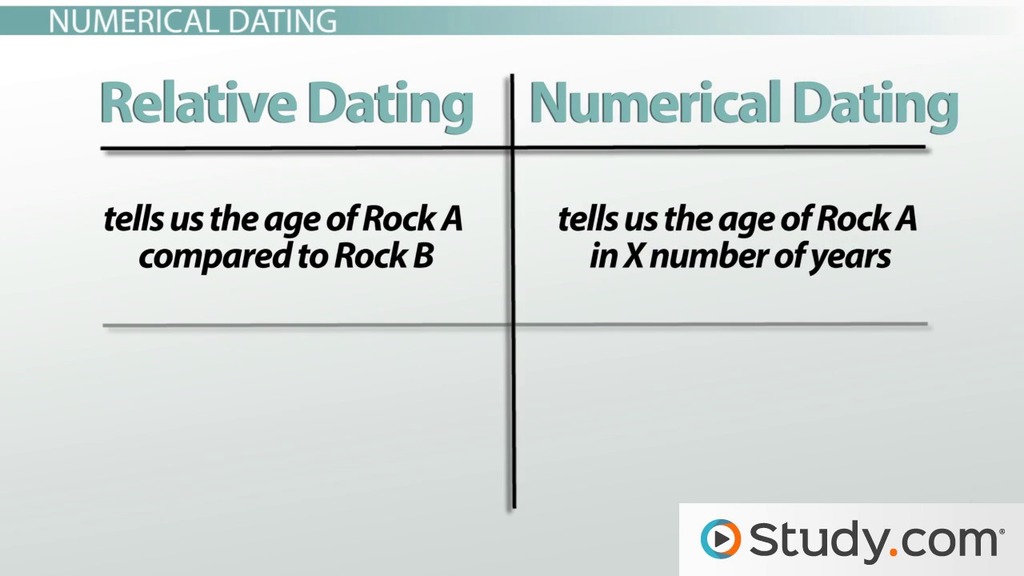
Numerical dating is when you are trying to determine how long ago something took place or specifically how old something or someone is. For example, the extinction of the dino … saurs about 65 million years ago. Relative dating cannot tell us how long ago something took place, only that is followed one event and preceded another. Absolute dating is the process of determining an approximate computed age in archaeology and geology..
Relative dating is determined by comparing its placement with that of … fossils in other layers of rock. In The Difference Between. Relative dating says that something happened a certain amount of years after something else happened. Absolute dating says that something happened in a certain yea … r.
It determines the period during which certain object was last subjected to heat. It is based on the concept that heated objects absorb light, and emit electrons. The emissions are measured to compute the age. Differentiation Using a Venn Diagram.
Navigation menu
A Venn diagram depicts both dating methods as two individual sets. The area of intersection of both sets depicts the functions common to both. Take a look at the diagram to understand their common functions. When we observe the intersection in this diagram depicting these two dating techniques, we can conclude that they both have two things in common: Provide an idea of the sequence in which events have occurred.
Determine the age of fossils, rocks, or ancient monuments. Although absolute dating methods determine the accurate age compared to the relative methods, both are good in their own ways.
Relative Dating vs. Absolute Dating: What's the Difference?
Relative Dating Techniques Explained. How are Waterfalls Formed. Types of Metamorphic Rocks. How are Rivers Formed? What Tools do Archaeologists Use. In archaeology, absolute dating is usually based on the physical, chemical, and life properties of the materials of artifacts, buildings, or other items that have been modified by humans and by historical associations with materials with known dates coins and written history. Techniques include tree rings in timbers, radiocarbon dating of wood or bones, and trapped-charge dating methods such as thermoluminescence dating of glazed ceramics.
In historical geology , the primary methods of absolute dating involve using the radioactive decay of elements trapped in rocks or minerals, including isotope systems from very young radiocarbon dating with 14 C to systems such as uranium—lead dating that allow acquisition of absolute ages for some of the oldest rocks on earth. Radiometric dating is based on the known and constant rate of decay of radioactive isotopes into their radiogenic daughter isotopes. Particular isotopes are suitable for different applications due to the types of atoms present in the mineral or other material and its approximate age.
For example, techniques based on isotopes with half lives in the thousands of years, such as carbon, cannot be used to date materials that have ages on the order of billions of years, as the detectable amounts of the radioactive atoms and their decayed daughter isotopes will be too small to measure within the uncertainty of the instruments.
What is the difference between absolute dating and relative dating
One of the most widely used and well-known absolute dating techniques is carbon or radiocarbon dating, which is used to date organic remains. This is a radiometric technique since it is based on radioactive decay. Carbon moves up the food chain as animals eat plants and as predators eat other animals.
- Pre/Post-Test Key?
- Categories!
- problems with dating a psychologist!
- dating a guy with no car!
- mobile app online dating!
- Relative Vs. Absolute Dating: The Ultimate Face-off.
- cooking speed dating!
With death, the uptake of carbon stops. It takes 5, years for half the carbon to change to nitrogen; this is the half-life of carbon After another 5, years only one-quarter of the original carbon will remain. After yet another 5, years only one-eighth will be left. By measuring the carbon in organic material , scientists can determine the date of death of the organic matter in an artifact or ecofact.
The relatively short half-life of carbon, 5, years, makes dating reliable only up to about 50, years. The technique often cannot pinpoint the date of an archeological site better than historic records, but is highly effective for precise dates when calibrated with other dating techniques such as tree-ring dating. An additional problem with carbon dates from archeological sites is known as the "old wood" problem.
What is Absolute Dating
It is possible, particularly in dry, desert climates, for organic materials such as from dead trees to remain in their natural state for hundreds of years before people use them as firewood or building materials, after which they become part of the archaeological record. Thus dating that particular tree does not necessarily indicate when the fire burned or the structure was built.
For this reason, many archaeologists prefer to use samples from short-lived plants for radiocarbon dating. The development of accelerator mass spectrometry AMS dating, which allows a date to be obtained from a very small sample, has been very useful in this regard. Other radiometric dating techniques are available for earlier periods. One of the most widely used is potassium—argon dating K—Ar dating. Potassium is a radioactive isotope of potassium that decays into argon The half-life of potassium is 1. Potassium is common in rocks and minerals, allowing many samples of geochronological or archeological interest to be dated.
Argon , a noble gas, is not commonly incorporated into such samples except when produced in situ through radioactive decay. The date measured reveals the last time that the object was heated past the closure temperature at which the trapped argon can escape the lattice. K—Ar dating was used to calibrate the geomagnetic polarity time scale.